Studio design- room within a room
- Tia Leoni Lewis
- Dec 14, 2015
- 12 min read
What is a room mode?
A room mode is the resonance frequency that are in a room. This is by an energy caused by an acoustic source such as a loud speaker or a guitar playing. Many rooms have a fundamental resonance in the range of 20 Hz to 200 Hz. Each frequency being related to one or more room’s dimensions or a divisor. For example if you had a panel that you could move around the room to be in any location. Why do we work out the room mode? Well this is so we know the room mode in the room we want to acoustically treat, maybe to turn it into a studio or into a production room. Or maybe both if you wanted to, keeping a lower budget. Working out the room mode will make it easier to know what the resonance frequency is of that room.
What is a resonance frequency? It is a phenomenon that occurs when a vibration system, caused by anything that produces waves of sound, or external force drives another system to oscillate with greater amplitude at a specific frequency.
"The increase in amplitude of oscillation of an electric or mechanical system exposed to a periodic force whose frequency is equal or very close to the natural undamped frequency of the system." (Ogata, 2005)
Above is a better definition of what a resonance is.
So we use this to work out the frequencies that are bad and good in a room. We can take a room and as showed below work out the room m ode and then we can use a tuner in the room that will work out those frequencies that the room doesn’t like or that doesn’t not go well In that room. Maybe vibrating too much or just sounding naff.
Some people who work in this industry of fine tuning a room and working out the room modes, are known to be very well paid so if you do your job properly then you could go into something well worth your while. Maybe it is something that you fine interesting. You can find things like this pretty much anywhere, could be that they are making a new building and want you to com in and work out what the room modes would be, you could get paid hell loads of money for this job.
What is RT60?
RT60 is a reservation time (how long it takes for sound to fade in a room). This is how long it takes the sound to decay 60dB in a large or small room. People debate at to the value of RT60 in a small room, or in rooms with an RT of less than 1 second as they are not realistically reverberant.
Reverb? What is it? It is literally like an echo. If you have a sound in a large space such as a theatre for example, then the sound will have more space to travel therefore the echo will remain longer and take longer to fade out. In a small room such as a studio for example the sound has less space in which to travel and therefor takes less time to decay. It is being absorbed by everything in the room quicker than that of in a theatre. This is why theatres are made to be more acoustically treated than other big spaces. This is also why studios are usually kept small with a lot of padding on the walls making it harder for the sound to go straight through the walls whereas with less sound proofing you could hear everything in the other room, and may be pic up sounds you may not want to hear on a recording. You also do this in a production room so you hear the purest of the recording without any interference from surroundings or anything like that. Which is why absorption things and diffusion panels are being used to acoustically treat a room.
Why do we work out RT60?
We work out the RT60, reverberation time in a room, to see how we need to acoustically treat it. For example if you have a bare room in your house, no furniture in it and the walls are bare and you want to create a studio of that room you would then need to add things into it to lower the fading sound time. This is because if you tried to record or produce in that room then it wouldn’t be very good to work in. this is why people use panels filled with foam or bass traps in the corner of the rooms to stop bass frequencies from piling up in the corners of the room. Knowing the reverberation time of a bare room will then allow you to add things into the room to acoustically treat it and then you work it out again and see how lon it takes for the sound roughly to decay. As shown below. My sound took a half a second in my room to lower and adding in some panels to treat it the sound decay level went down by 5 milliseconds. Surprisingly it may not seem like much but a little can make a big difference.
How to make a home studio?
When it comes to making a studio at home or anywhere for that matter, you need to know the basics and the needs of how to create a studio. You will need to know where the room will be. How big you want it to be to work out the reverberation time, and just generally how big the room is. You do this with the equation 0.161 x volume of space / surface area of the elements in the room x absorption co-efficient. If you know how to di this then it will be quiet simple. However first you will need to work out the volume of your space to work out the reverberation time. And you will also need to know the material for everything in the room. (Walls, ceiling, floor etc... What everything is made from)?
Below is the absorption co-efficient:
This is a picture of all of the absorption co-efficient numbers of all of the material in the room I am working on. For the calculations below I have used the htz as 1khtz.
Notice how the absorption levels change in what Hz you are in. lower in some areas more than others. Anything you change can impact on its outcome either drastically or just a little bit.
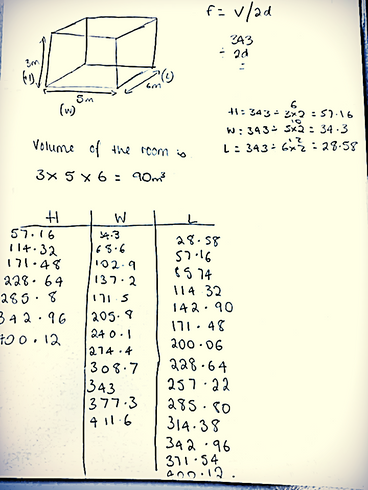
Below will be a picture of how to work out the axial room mode:
This is the room modes. This is just the room not including the door or the window in the second picture.
Below is a picture of the RT60 which is the reverberation time of the surface area of the room:
(Before acoustic treatment)
This is the really complicating bit. This is where you take everything you worked out before. And then use that information to work out the reverberation time of the room. This is done by working out the surface area of each dimension, meaning the walls and the floor and ceiling. Whereas before I didn’t have the window and door, I now have to deduct the window and the door from the surface area of two walls. Then after you have done all of this you will need to add up all of the ending calculations of the walls surfaces. And then use the equation on the top of the sheet and divide the answer from 0.161 x 90 which is 14.49 by the surface area x absorption time added together which is 24.87. You divide these and that comes up with the answer for the reverberation time. Reverberation time is where the length of reverb lasts. Reverb is basically echo. You can change this. If you are in a small room it won’t be very echoy, whereas if you are in a massive theatre and it is king of bare the sound will bounce around everywhere off of everything and that is called reverb/echo.
With this information you then know how much editing you need to do to that room to make it more dead for recording the most plane and original sound from vocals or instruments.
How to improve my room?
If I wanted to improve my room I would have to put in some sound proofing.
One way you would do this is by a floating floor. This is done by raising the room higher than the foundation and then it acts as an air pocket. This would help with making sure that there is no vibrations passing through the floor that is not being absorbed through the floor. Y this I mean if you had a normal room without it being raised then it would be able to absorb any of the sound because it has no space under it, whereas when you have space under the floor it is more likely to absorb some of the sound.
In the corner of the rooms you may also have bass traps because the corner of the room is where bass likes to collect so having a bass trap will remove this. And make the air sound more clear. You b will however still hear the bass but the bass that the microphone that you use will capture.
Why do we need absorption and diffusion?
All sound travels. No matter what direction or at what speed through what atmosphere or object it will always travel. Sound will also be absorbed and reflected in different ways.
We need these things to make the rom more suitable for recording and editing music and anything that is recorded. For recording the best thing for you to do is make sure that the room is not TOO DEAD and that the room is still active with the slightest bit of sound, but dead enough that there is not any background sounds while recording anything in the recording space. If a room tends to be too dead then a human can actually go insane because they will start hearing there organs in their body working, which then makes them go insane. So a tip is to make sure that the room is dead but not too dead.
What is absorption?
Absorption is something in which you need to be able to make a room deader. This is done by adding things into the room to take away the amount of reverb in the room. This will also make the reverberation time shorter making it more fit to record in.
You would do this by adding in furniture or panels on the walls. Things like a sofa or pillows. A board or foam panels on the walls ceiling and carpets on the floor to absorb some of the sound created.
You could also add in panels that fit snug into the corners of your room. This is because bass frequencies tend to collect in the corner of a room so we install something which is called a bass trap. This will capture some of the bass sound that is collected in the corner of the room. However this does not mean that you won’t have any bass sound in your recording. This will picked up by the microphone capturing what you are recording so you will still get bass captured just won’t be all over the place. Same as the bass trap the diffusion panels will point the bass around the room in different directions making it sound slightly more different.
Some people will be able to have something to use as absorption material that they use every day. This includes things like a sofa or a mattress. Or even a rug for the floor. You could even get a rug and use it as a decoration on the wall but then people won’t actually realise that the rug is being used for absorption.
What is diffusion?
Diffusion is something in which makes the sound travel around the room in a certain way. This will also make the sound travel more widely ( (Anon., 2015) )in the room and make it all go in different directions being spread widely instead of just bouncing off a smooth flat surface. This may also minimize the amount of build-up of bass in the corners, which wouldn’t be so bad considering you can just add a bass trap in the corner of the room, trapping the bass from being stuck in the corner.
This is how someone has added diffusion into a room. If you see the textured panel on the ceiling and the panels on the walls, they both have a certain pattern. This is so that they sound bounces of this but is manipulated in a certain way. Some are pointing in different angles making the sound travel in a certain direction.
You can also use things like a bookcase for example as a way of diffusion. You can also create it by putting different sized books in the book case and add different spaces between them all. This is so the sound can travel in all different directions.
Something that people will also use for diffusion is a bookcase. This will also absorb some things but the hard surface reflects sound if you like. So instead of using something like a scatter board or a BAD (binary, Amplitude Diffusion panel, you can just use a bookcase. This is something that pretty much most people will have in their room anyway regardless where it may be in the house.
Tuning a room.
What does it mean when you tune a room? Well the best way to describe it is that you work out the frequencies that you room, if you like doesn’t like, or that will make the room shake, and you then find the frequencies, and you make an EQ track and find the frequencies on the EQ and then turn them down so anything being done in that room is not being disturbed by the frequencies that may shake your room. Then while you are getting ready to record anything in that room you can just add that saved EQ onto the master track and it will get rid of those frequencies making it more suitable to record without having any feedback in that room, making your recording low quality.
Speaker placement.
In a home studio the speaker placement is really important. While being behind the computer that you will be EQing and editing at and then if the speakers are not in the right place the sound won’t be the best. You won’t be able to hear the purity of the sound.
The layout of the speakers has to be 3 ft from everything meaning each other and your head. Making sure they are pointing towards you to make sure you have the purest of the sound. Making sure they are slightly tilted inwards towards your head. This makes sure they are pointing to each one of your ears. The way to remember it is to make an equilateral triangle with you and your speakers. This will ensure that they are in the right place because the length and the angles are the same. Everything is equal. This is a very simple diagram of where the speakers should be placed to ensure the best results in the playback.
This is the room when it is being treated.
After I have added in some foam panels into the room, I worked out the RT60 again and then worked out the reverberation time after sound proofing it. Because the 50 mm foam panel the reverberation time has changed from being 0.58 seconds to 0.53 seconds, so it has changed the reverberation time by 5 milliseconds. So by adding in panels my room is getting better for producing in.
However if I added a bookcase and placed randomly placed books and book sizes in it the reverberation time would then change again because not only would the diffusion change the direction of the sound but it would then also change the reverberation time because everything absorbs sound. Weather that is just a little bit the tiniest bit or a lot, everything absorbs sound.
I have placed the panels where they are because sound tends to reflect of everything, and flat surfaces where the sound bounces off of. Placing the panels on the walls around in the room (2 in this case) makes it easier to absorb sound. This helps because it means that the reverberation time is minimalized and the room is a little bit more dead which makes it easier to work in and produce. This will also help the speakers where you place them.
For making the room more dead and adding things that are to make the room deader, you could add curtains on the windows or just the walls and also add a rug on the floor. You would then work out the reverberation time of the room after doing this by doing it the same way you would do everything else. Just by adding everything together and taking the rug or curtains away from the surface area it is on. For example work out the area of the floor and then deduct the area of the rug. Then after you have done this you would then just work out how much the rug would absorb and the same for the floor and everything else and then you add them altogether as normal and that is then your reverberation time. Then you divide the volume of the space by that number which would then make the new reverberation time. You would use these objects because of the absorption level and this will improve the sound proofing of the room.
If you have a certain reverberation time that you want to achieve you would just keep sound proofing the room and adding in more things to absorb some of the sound and then keep working it out until you have had the desired reverberation time.
And that is how you treat the room and work out the reverberation time of the room after it has been treated. If you practice it then it gets easier and easier to work out.
References
Anon., 2015. google. [Online] Available at: http://www.bing.com/search?q=diffusion+definition+in+the+studio&qs=n&form=QBRE&pq=diffusion+definition+in+the+studio&sc=0-23&sp=-1&sk=&cvid=f6d9d43ecf74496a8fc5b563414ab0d7
Ogata, K., 2005. System Dynamics. 4th ed. University of Minnesota: s.n.
Here are a few images from Robs assignment that i have recently been working on and finished.






































Comments